When you run a business, keeping your employees safe should be a top priority, especially when hazardous chemicals are involved. Whether you’re subject to OSHA regulations in the United States or WHMIS requirements in Canada, proper hazard communication is essential for workplace safety and regulatory compliance.
This guide breaks down what we call the “HazCom Pentagon”—five critical elements that form a complete hazard communication program. By understanding and implementing these key components, you’ll create a safer workplace while meeting compliance requirements in both U.S. and Canadian jurisdictions.
To help you get started, we’ve created a free Hazard Communication Plan template that addresses all five elements. Download it now to take the first step toward comprehensive chemical safety management.
Download Your Free HazCom Plan Template:

What is Hazard Communication Compliance?
Hazard communication compliance is a critical component of workplace safety, ensuring employees understand the chemicals they may encounter and how to protect themselves from potential hazards. By implementing a comprehensive hazard communication program, employers create a safer work environment and reduce the likelihood of chemical-related injuries or illnesses.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) mandates hazard communication through its Hazard Communication Standard (HCS). Canadian employers follow similar requirements under the Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS). Both regulatory frameworks align with the Globally Harmonized System (GHS), which provides a unified approach to chemical classification and labeling worldwide.
Goals of Hazard Communication Compliance
A properly implemented hazard communication program serves several important purposes:
- Protecting workers from chemical exposure
- Ensuring employees know how to handle hazardous materials safely
- Promoting a safer workplace environment by fostering awareness and preparedness
- Reducing workplace injuries and fatalities related to improper chemical handling
- Access to critical chemical information in an emergency response
The five elements of our “HazCom Pentagon” work together to create a complete compliance program that not only satisfies regulatory requirements but genuinely protects your workforce. Each element reinforces the others, creating a comprehensive safety system that addresses all aspects of chemical safety in your workplace.
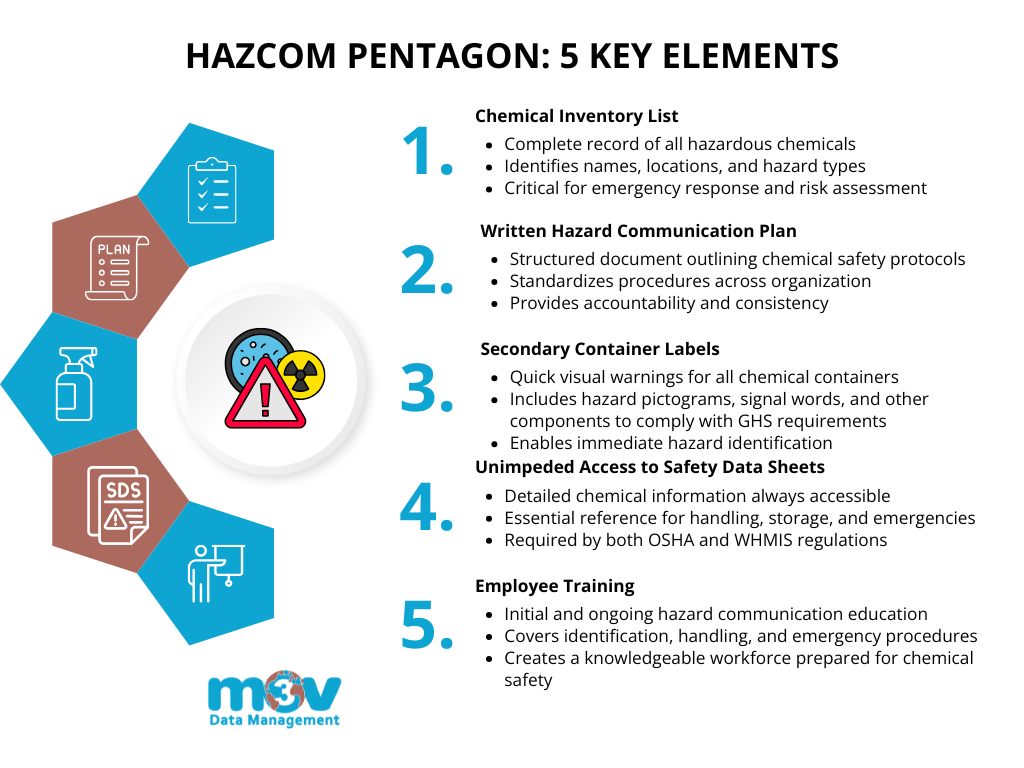
5 Steps of Hazard Communication Compliance
A strong hazard communication program is built on five key elements, ensuring that employees are informed, prepared, and protected from potential chemical hazards in the workplace.
1. Chemical Inventory List
A chemical inventory list is a detailed record of all hazardous chemicals used, stored, or transported within a workplace. This list should include each chemical’s name and location, ensuring that employees and safety personnel can quickly access this information when needed. Regular updates are essential to ensure accuracy and compliance with OSHA and WHMIS regulations.
Keeping an up-to-date chemical inventory is more than just an organizational tool—it is a workplace safety necessity. A well-maintained inventory helps identify hazardous substances and assess the risks they pose to workers. This ensures safe storage and handling of chemicals to prevent accidents, spills, or regulatory violations. It also provides first responders with critical information in case of a chemical spill, fire, or exposure incident.
Actions for Employers:
- Keep an up-to-date inventory, including hazard classifications and safety measures.
- Conduct routine audits to ensure new chemicals are added and outdated or unused chemicals are safely disposed of.
- Ensure your inventory list is accessible so that employees and safety personnel can reference the inventory when needed.
2. Written Hazard Communication Plan – Download a Free Template Today Using the Submission Above!
A written hazard communication plan is a critical document that outlines how a company manages chemical hazards, ensuring employees understand labeling, Safety Data Sheets (SDS), and proper training protocols. This plan serves as a structured guide for maintaining workplace safety and compliance with OSHA and WHMIS regulations. It must be accessible to all employees and updated regularly to reflect changes in workplace hazards or chemical usage.
Having a written hazard communication plan is more than a compliance requirement—it provides clarity, consistency, and accountability in handling hazardous materials. A well-documented plan standardizes hazard communication across the organization, defines clear procedures for labeling, SDS maintenance, and employee training.
Actions for Employers:
- Develop and document a structured program detailing how chemical hazards will be communicated.
- Specify procedures for labeling, SDS management, and employee training.
- Regularly review and update the plan to align with new regulations or workplace changes.
3. Secondary Container Labels and Labeling Requirements
Proper chemical labeling is essential for workplace safety, ensuring employees can quickly identify hazardous materials and take the necessary precautions. Secondary container labels provide critical information about chemical hazards, including hazard symbols, signal words, and precautionary statements. These labels must be clear, visible, and readable in any area where chemicals are stored or used.
Clear labels should communicate essential hazard information at a glance, reducing the risk of accidental exposure or misuse. They help ensure compliance with the 29 CFR 1910.1200 HCS and WHMIS to ensure consistency and clarity in hazard communication. This will improve workplace safety by reinforcing proper handling procedures and emergency response measures.
Each hazardous chemical container should have:
- A product identifier
- An appropriate signal word (e.g., Danger, Warning)
- Hazard statements describing the nature and severity of the hazard
- Pictograms representing specific hazards
- Precautionary statements for safe handling and emergency response
- The name, address, and telephone number of the manufacturer, importer, or responsible party
Actions for Employers:
To maintain compliance and safety, employers should:
- Ensure all chemicals are labeled with the required hazard information.
- Regularly inspect labels to confirm they remain legible and intact.
- Update labels whenever new safety information becomes available or regulations change.
Download our Hazard Communication Standard Pictogram here. Use this as a training resource, or a way to visually communicate hazards associated with chemicals in the workplace.
4. Unimpeded Access to Safety Data Sheets
Safety Data Sheets (SDS) provide essential information about hazardous chemicals, including their composition, physical and chemical properties, health risks, and emergency response measures. These documents serve as a go-to resource for employees who need to understand chemical hazards and follow proper handling procedures. OSHA requires that SDS be readily available at all times to workers and emergency responders.
SDS’s ensure employees have access to detailed, accurate information about chemical hazards before handling them. This provides essential safety guidance, helps workers make informed decisions about chemical handling and storage, and compliance with OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard.
Actions for Employers:
- Ensure SDS are easily accessible in areas where chemicals are used and stored
- Review and update SDS regularly to reflect the latest safety information
- Train employees on how to read and interpret SDS effectively
5. Employee Training
Employee training is a crucial component of workplace safety, ensuring that workers are properly educated on chemical hazards, labeling systems, and emergency procedures. This training is not a one-time event—it must be ongoing and updated whenever new chemicals are introduced or regulations change. OSHA requires that employers provide hazard communication training upon hiring and conduct annual sessions to keep employees informed and prepared.
Comprehensive training helps employees safely handle hazardous materials by understanding proper storage, usage, and disposal. Employees can then recognize and respond to emergencies involving chemical spills, fires, or accidental exposure, reducing the risk of workplace injuries.
Actions for Employers:
To ensure compliance and workplace safety, employers should:
- Provide initial and annual hazard communication training for all employees.
- Cover all aspects of chemical safety, including proper handling, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), emergency response protocols, and SDS interpretation.
- Maintain training records to track employee participation and ensure ongoing compliance.
Investing in regular employee training not only meets regulatory requirements but also creates a safer, more knowledgeable workforce, reducing workplace risks and improving overall safety culture.
Strengthening Your HazCom Plan with M3V’s SDS Management
Managing Safety Data Sheets is a critical cornerstone of your HazCom Pentagon. Without effective SDS management, even the best chemical safety program can collapse. That’s where M3V Data Management makes a difference.
Our specialized SDS management software transforms how you handle this essential element of hazard communication compliance:
- Instant Access: Provide employees with immediate access to crucial safety information from anywhere in your facility
- Automatic Updates: Receive the latest manufacturer SDS versions without manual searching or requests
- Simplified Compliance: Generate compliant secondary container labels directly from your SDS database
- Emergency Preparedness: Enable first responders to quickly access critical chemical information during incidents
- Audit Readiness: Maintain organized records that demonstrate compliance during inspections
SDS management shouldn’t be your biggest workplace challenge. Let M3V handle this cornerstone of your HazCom Pentagon, so you can focus on what matters most: running your business and keeping your team safe.
Sources:
https://www.osha.gov/hazcom
https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/publications/OSHA3696.pdf
https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/learning/safetyculturehc/module-5/7.html
https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/publications/OSHA3514.pdf
https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/environmental-workplace-health/occupational-health-safety/workplace-hazardous-materials-information-system.html
https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/regulations/standardnumber/1910/1910.1200





